In Steven Sinofsky’s this blog – Bringing Hyper-V to “Windows 8”. He talks about that Windows 8 will support virtualization on the “client” OS. This is very helpful for developers as they typically have the need to setup additional test environment on their PC/Laptop.
Hardware Requirements
Hyper-V supports creation of both 32-bit and 64-bit operating systems in VMs. To run Client Hyper-V, your computer must:
- Be running a 64-bit version of Windows 8.
- Have a CPU that supports Second Level Address Translation (SLAT), To determine if your CPU supports SLAT, go to How to tell if your CPU Supports SLAT
Enabling Client Hyper-V
- In the Windows 8 Control Panel, tap or click Programs, and then tap or click Programs and Features.
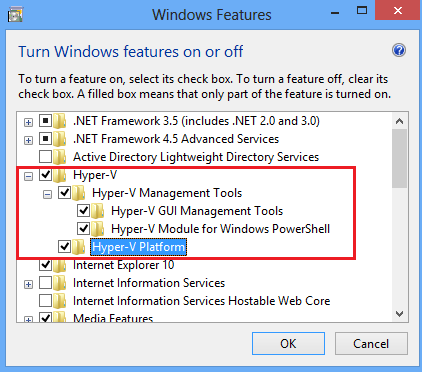
- Tap or click Turn Windows features on or off.
- In the Windows Features dialog box, select the check boxes for the Hyper-V items that you want to install, and then tap or click OK.
- Tap or click Close.
Note: You must restart your computer to complete the Hyper-V installation. After restarting the computer, you can use Hyper-V Manager or Windows PowerShell to create and manage VMs. You can also use VM Console to connect to VMs remotely.
Enabling Client Hyper-V with Command Line Tool
-
Use Windows PowerShell. At the Windows PowerShell prompt (using administrator credentials), type the following:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V
- Use the Windows Command Prompt. At the Windows command prompt (using administrator credentials), type the following:
Dism /online /enable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Hyper-V –All
What Isn’t Included in Client Hyper-V?
Difference between Windows 8 Client Hyper-V and Server Hyper-V
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.