SLAT-enabled processor is the requirement of Hyper-V RemoteFX feature which is introduced in Windows Server 2008 R2. It’s the requirement of Windows 8 client Hpyer-V feature as well.
For INTEL CPU models, following CPU models are SLAT-Capable
- Server: E5500 or higher.
- Desktop/Laptops: I3/I5/I7/I7-qm
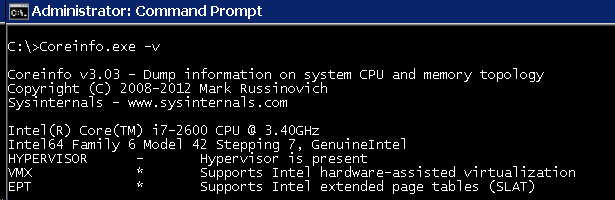
There is a handy tool named CoreInfo from systeminternals that can check if your CPU is SLAT-Capable, it’s pretty easy to use:
- Download from http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/cc835722
- Launch an elevated command prompt
- Run “CoreInfo.exe -v”
If you see EPT * Supports Intel extended page tables (SLAT) then you are good.
Following are copied from https://social.technet.microsoft.com/wiki/contents/articles/1401.hyper-v-list-of-slat-capable-cpus-for-hosts.aspx
Servers that support SLAT
- Any AMD server CPU based on Barcelona or later architectures. Some early Barcelona editions didn’t have RVI, but they’re relatively rare. Check this AMD list.
- Intel server processors numbered E5500 and higher.
- Any Intel CPUs based on Nehalem, Westmere, or Sandybridge micro-architectures. (There may be exceptions, but I’m not aware of any.)
Desktops that support SLAT
- Intel processors whose names start with ‘i’, e.g. i3, i5, i7, i9. (There may be exceptions, but I’m not aware of any.)
- Any Intel CPUs based on Nehalem, Westmere, or Sandybridge micro-architectures. (There may be exceptions, but I’m not aware of any.)
Laptops that support SLAT
- Lenovo T410, T510, W510, W520, T420s, T520, X201
- Samsung 900x
- Dell Precision M4600