IIS 7 / 7.5 / 8
On IIS 7 / 7.5 / 8, configure website or web application to run under 32 bit mode can be configured by opening a command prompt and typing following command and press ENTER.
%windir%system32inetsrvappcmd set config -section:applicationPools -applicationPoolDefaults.enable32BitAppOnWin64:true
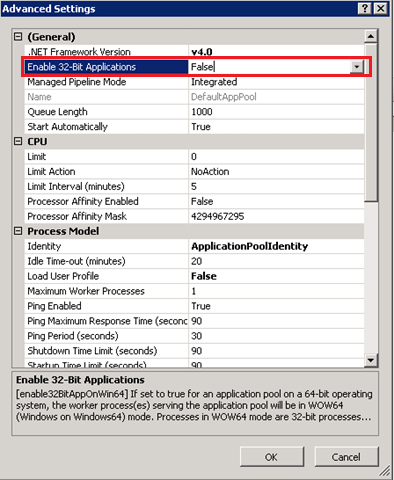
You can achieve the same goal in IIS Manager by opening the ‘Advanced Settings’ on the application pool binded to the website/web application you want to run under 32 bit mode and change “Enable 32-bit Applications” to True
Click okay and now the web application or website you configured will run under 64-bit mode always.
IIS 6
For IIS6 on Windows Server 2003, configure ASP.NET to run in 32 bit mode on a 64 bit windows server.open a command prompt and type following command and press ENTER.
cscript //nologo %SYSTEMDRIVE%InetPubAdminScriptsadsutil.vbs set w3svc/AppPools/Enable32bitAppOnWin64 1
In IIS 6, you cannot run one Application Pool in 32-bit and others in 64-bit. But you can do this on IIS 7 and later as Enable32BitAppOnWin64 can be configured per application pool since IIS 7.